


Similar term(s): Di-n-butyl phthalate, DNBP, Butyl phthalate, n-Butyl phthalate.
DBP, also known as DNBP, is a phthalate with the same core structure as DIDP and DINP but with two shorter side chains attached, each having four carbon atoms.
In the 1990s, over 75% of DBP was used as plasticiser in plastics such as PVC, 14% in adhesives, 7% in printing inks and 3% in other miscellaneous uses, including sealants and grouting agents used in construction as well as consumer products. For instance, it was used as an additive to perfumes, deodorants, hair sprays, nail polish, printer inks, and insecticides.
At present, DBP is banned in all toys and childcare articles (see European Directive 2005/84/EC) as well as in cosmetics, including nail polish as it is considered to be carcinogenic, mutagenic or toxic to reproduction (CMR-substance) (see European Cosmetics Directive).
Source: Based on the GreenFacts study on Phthalates
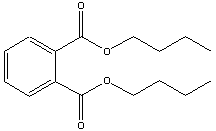
Source: GreenFacts
GreenFacts Summary on Phthalate Di-butyl phthalate:
GreenFacts Summary on Phthalates in school supplies:
Deutsch: Dibutylphthalat (DBP)
Español: Dibutilftalato (DBP)
Français: Phtalate de Dibutyle (DBP)