


Adjustment in natural or human systems to a new or changing environment.
Various types of adaptation can be distinguished, including anticipatory and
reactive adaptation, private and public adaptation, and autonomous and planned
adaptation.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
![]()
Breeding and rearing of fish, shellfish, or plants in ponds, enclosures, or
other forms of confinement in fresh or marine waters for the direct harvest of
the product.
(Source:
MA
![]()
The mass of air surrounding the Earth.
The atmosphere consists of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and traces of other gases such as argon, helium, carbon dioxide, and ozone.
The atmosphere plays an important role in the protection of life on Earth; it absorbs ultraviolet solar radiation and reduces temperature extremes between day and night. (Source: GreenFacts)
Biodiversity is a contraction of biological diversity. Biodiversity reflects the number, variety and variability of living organisms.
It includes diversity within species (genetic diversity), between species (species diversity), and between ecosystems (ecosystem diversity). (Source: GreenFacts)
A process of strengthening or developing human resources, institutions, organizations, or networks.
Also referred to as capacity development or capacity enhancement.
(Source:
MA,
![]()
A colorless, odorless, non-combustible gas, present in low concentrations in the air we breathe (about three hundredths of one percent by volume).
Carbon dioxide is produced when any substance containing carbon is burned. It
is also a product of breathing and fermentation. Plants absorb carbon dioxide
through photosynthesis.
(Source: The Pacific Forest Trust
Glossary![]()
The long-term fluctuations in temperature, precipitation, wind, and all other aspects of the Earth's climate.
It is also defined by the United Nations Convention on Climate Change as
“change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity
that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to
natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods”
(Source:
CoRIS
glossary![]()
When referring to humans, a community is defined as:
A collection of human beings who have something in common.
A local community is a fairly small group of people who share a common place of residence and a set of institutions based on this fact, but the word ‘community’ is also used to refer to larger collections of people who have something else in common (e.g., national community, donor community).
When referring to other living organisms, a community is defined as:
An assemblage of species occurring in the same space or time, often linked by
biotic interactions such as competition or predation.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
![]()
"Governments worldwide have promised to save biodiversity by 2010. Countdown 2010 helps them move from words to action."
"Objectives:
A persistent reduction in the capacity to provide ecosystem services.
(Source:
MA
![]()
Land degradation in drylands resulting from various factors, including climatic variations and human activities.
Land degradation in drylands resulting from various factors,
including climatic variations and human activities.
(Source:
MA ![]()
Usually a numerical measure of quality of life in a country.
Indicators are used to illustrate progress of a country in meeting a range of economic, social, and environmental goals.
Since indicators represent data that have been collected by a variety of
agencies using different collection methods, there may be inconsistencies among
them.
(Source: Global education Globalisation
glossary![]()
The variety and relative abundance of different entities in a sample.
(Source:
MA
![]()
Dryland systems are ecosystems characterised by a lack of water. They include cultivated lands, scrublands, shrublands, grasslands, savannas, semi-deserts and true deserts.
The lack of water constrains the production of crops, forage, wood, and other ecosystem services.
Four dryland subtypes are widely recognized: dry sub-humid,
semiarid, arid, and
hyperarid, showing an increasing level of aridity or moisture
deficit.
(Source: GreenFacts based on Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
![]()
Any variation in the state, outputs, or structure of an ecosystem.
(Source:
MA
![]()
An approach to natural resource management which aims to sustain ecosystems to meet both ecological and human needs in the future. (Source: GreenFacts)
The benefits people obtain from ecosystems.
These include provisioning services such as food and water; regulating
services such as flood and disease control; cultural services such as spiritual,
recreational, and cultural benefits; and supporting services such as nutrient
cycling that maintain the conditions for life on Earth.
(Source:
MA
![]()
The complex system of plant, animal, fungal, and microorganism communities and their associated non-living environment interacting as an ecological unit.
Ecosystems have no fixed boundaries; instead their parameters are set to the
scientific, management, or policy question being examined. Depending upon the
purpose of analysis, a single lake, a
watershed, or an entire region could be
considered an ecosystem.
(Source:
US EPA
Glossary of Climate Change Terms
![]()
A natural process in which elements are continuously cycled in various forms between different compartments of the environment (e.g., air, water, soil, organisms).
Examples include the carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles (nutrient cycles) and the water cycle. (Source: GreenFacts)
Fairness of rights, distribution, and access. Depending on context, this can
refer to resources, services, or power.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
![]()
"The European Commission (EC) embodies and upholds the general interest of the [European] Union and is the driving force in the Union's institutional system. Its four main roles are to propose legislation to Parliament and the Council, to administer and implement Community policies, to enforce Community law (jointly with the Court of Justice) and to negotiate international agreements, mainly those relating to trade and cooperation."
The Commission's staff is organised into 36 Directorates-General (DGs) and
specialised services, such as the Environment DG and the Research DG.
(Source:
EC website![]()
The increase in additions of nutrients [especially nitrogen and phosphorus] to
freshwater or marine systems, which leads to increases in plant growth and often
to undesirable changes in ecosystem structure and function.
(Source:
MA
![]()
"The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and debate policy. FAO is also a source of knowledge and information. We help developing countries and countries in transition modernize and improve agriculture, forestry and fisheries practices and ensure good nutrition for all. Since our founding in 1945, we have focused special attention on developing rural areas, home to 70 percent of the world's poor and hungry people. FAO's activities comprise four main areas:
Water that is not salty, for instance water found in lakes, streams, and rivers, but not the ocean. Also used to refer to things living in or related to freshwater (e.g., "freshwater fish"). (Source: GreenFacts)
The Global Mechanism is a subsidiary body of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification. As one of the partners in Convention implementation, it provides a range of specialized financial advisory services to the Parties, with the aim of increasing development finance for poverty reduction by promoting sustainable land management.
(Source: The Global Mechanism website![]()
The geographical realm encompassing all of Earth.
(Source:
MA
![]()
The increasing integration of economies and societies around the world,
particularly through trade and financial flows, and the transfer of culture and
technology.
(Source:
MA
![]()
Water beneath the Earth's surface in the spaces between soil particles and
between rock surfaces.
(Source:
ATSDR
Glossary of
Terms![]()
The location and environmental conditions in which a particular organism normally lives.
(Source:
MA
![]()
Inland waters are permanent water bodies inland from the coastal zone and areas whose properties and use are dominated by the permanent, seasonal, or intermittent occurrence of flooded conditions.
Inland waters include rivers, lakes, floodplains, reservoirs, wetlands, and inland saline systems. (Source: MA Synthesis Report )
"A public corporation, IDRC was created by the Parliament of Canada in 1970.
IDRC's mandate, as stated in the International Development Research Centre Act, is:
To initiate, encourage, support, and conduct research into the problems of the developing regions of the world and into the means for applying and adapting scientific, technical, and other knowledge to the economic and social advancement of those regions.
In doing so, the Centre helps developing countries use science and knowledge to find practical, long-term solutions to the social, economic, and environmental problems they face."
(Source: IDRC Website![]()
"The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), a specialized agency of the United Nations, was established as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference.
IFAD's mission is to enable the rural poor to overcome poverty.
IFAD is dedicated to eradicating rural poverty in developing countries. IFAD focuses on country-specific solutions, which can involve increasing rural poor peoples' access to financial services, markets, technology, land and other natural resources."
(Source: IFAD website![]()
The human use of a piece of land for a certain purpose (such as irrigated agriculture or recreation). Influenced by, but not synonymous with, land cover.
(Source:
MA
![]()
An area of land that contains a mosaic of ecosystems, including human-dominated ecosystems.
The term cultural landscape is often used when referring to
landscapes containing significant human populations or in which there has been
significant human influence on the land.
(Source:
MA
![]()
Macro Policy is policy which affects the whole country [or region].
It is concerned with monetary, fiscal, trade and exchange rate conditions as well as with economic growth, inflation and national employment levels.
It is distinct from micro policy which only affects particular sectors,
districts, neighbourhoods or groups.
(Source: Livelihoods Connect Glossary
![]()
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), endorsed by governments at the United Nations in September 2000, aim to improve human well-being by reducing poverty, hunger, child and maternal mortality, ensuring education for all, controlling and managing diseases, tackling gender disparity, ensuring sustainable development and pursuing global partnerships.
The eight MDGs are:
Goal 1: Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
Goal 2: Achieve universal primary education
Goal 3: Promote gender equality and empower women
Goal 4: Reduce child mortality
Goal 5: Improve maternal health
Goal 6: Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other disease
Goal 7: Ensure environmental sustainability
Goal 8: Develop a global partnership for development
(Source: GreenFacts, based on the
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
)
"The MA is an international work program designed to meet the needs of decision makers and the public for scientific information concerning the consequences of ecosystem change for human well-being and options for responding to those changes.
The MA was launched by U.N. Secretary-General Kofi Annan in June 2001 and it will help to meet assessment needs of the Convention on Biological Diversity, Convention to Combat Desertification, the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, and the Convention on Migratory Species, as well as needs of other users in the private sector and civil society.
If the MA proves to be useful to its stakeholders, it is anticipated that an
assessment process modeled on the MA will be repeated every 5–10 years and that
ecosystem assessments will be regularly conducted at national or sub-national
scales."
(Source:
MA website![]()
A measure of frequency of occurrence of death in a defined population during
a specified interval of time.
(Source:
CDC
Reproductive Health Glossary
![]()
The approximately 20 chemical elements
known to be essential for the growth of living organisms, including nitrogen,
sulfur, phosphorus, and carbon.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
Glossary
![]()
A group or number of people living within a specified area or sharing similar
characteristics (such as occupation or age).
(Source:
ATSDR
Glossary of
Terms![]()
The pronounced deprivation of well-being.
Income poverty refers to a particular formulation expressed solely in terms of
per capita or household income.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
![]()
Production is the process of creating, growing, manufacturing, or improving goods and services. It also refers to the quantity produced.
In economics, productivity is used to measure the efficiency or rate of production. It is the amount of output (e.g. number of goods produced) per unit of input (e.g. labor, equipment, and capital).
In biology, productivity is a measure of the efficiency with which a biological system converts energy into growth. (Source: GreenFacts)
A good or service in which the benefit received by any one party does not
diminish the availability of the benefits to others, and where access to the
good cannot be restricted.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ![]()
Regionalization is the tendency to form regions or the process of doing so.
When used in opposition to globalization, this often means a world that is less connected, with a stronger regional focus. (Source: GreenFacts)
The buildup of salts in soils.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ![]()
A plausible and often simplified description of how the future may develop, based on a coherent and internally consistent set of assumptions about key driving forces (e.g., rate of technology change, prices) and relationships.
Scenarios are neither predictions nor projections and sometimes may be based on a “narrative storyline.”
Scenarios may include projections but are often based on additional
information from other sources.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ![]()
Place where seeds are stored for short-term use in farming or for long-term preservation. (Source: GreenFacts )
Rock worn into tiny pieces (coarser than clay, but finer than sand). It is
found sometimes as the deposit of sediment at the mouth of a river.
(Source: Ecohealth
Glossary
![]()
A group of organisms that differ from all other groups of organisms and that
are capable of breeding and producing fertile offspring. This is the smallest
unit of classification for plants and animals.
(Source:
OceanLink
Glossary of Common Terms and Definitions in Marine
Biology![]()
Individuals or groups that are affected by a decision and have an interest in
its outcome.
(Source:
TDM Encyclopedia
Glossary
![]()
Financial assistance (often from governmental bodies) to businesses, citizens, or institutions to encourage a desired activity deemed beneficial. (Source: GreenFacts)
A characteristic or state whereby the needs of the present and local population can be met without compromising the ability of future generations or populations in other locations to meet their needs.
"Poverty reduction and sustainable development are the principal tasks of the SDC. To facilitate the achievement of these goals, the SDC focuses on various thematic priorities. In each thematic domain, a sub-goal is targeted while ever keeping in mind the fact that the priority themes are intimately linked to one another."
(Source: SDC website![]()
When the combined effect of several forces operating is greater than the sum
of the separate effects of the forces.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ![]()
TerrAfrica is a partnership that aims to address land degradation by scaling up harmonized support for effective and efficient country-driven Sustainable Land Management (SLM) practices in sub-Saharan African countries.
(Source: TerrAfrica website![]()
The level of magnitude of a system process at which sudden or rapid change
occurs.
(Source:
PhysicalGeography.net
Glossary of
terms![]()
A pattern of change over time, over and above short-term fluctuations.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
![]()
"In 1992, the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) or so called Rio Earth Summit recommended the elaboration of a United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD). The Convention, the only convention stemming from a direct recommendation of the Conference's Agenda 21, was adopted in Paris on 17 June 1994 and entered into force in December 1996. It is the first and only internationally legally binding framework set up to address the problem of desertification. The Convention is based on the principles of participation, partnership and decentralization - the backbone of Good Governance. It now has more than 180 country Parties to the Convention, making it truly global in reach."
(Source: UNCCD website![]()
"The United Nations was established on 24 October 1945 by 51 countries committed to preserving peace through international cooperation and collective security. Today, nearly every nation in the world belongs to the UN: membership totals 191 countries*.
When States become Members of the United Nations, they agree to accept the obligations of the UN Charter, an international treaty that sets out basic principles of international relations. According to the Charter, the UN has four purposes: to maintain international peace and security; to develop friendly relations among nations; to cooperate in solving international problems and in promoting respect for human rights; and to be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations."
(Source: UN website![]()
"UNDP is the UN's global development network, an organization advocating for
change and connecting countries to knowledge, experience and resources to help
people build a better life. We are on the ground in 166 countries, working with
them on their own solutions to global and national development challenges. As
they develop local capacity, they draw on the people of UNDP and our wide range
of partners."
(Source:
UNDP website![]()
"Today, UNESCO functions as a laboratory of ideas and a standard-setter to
forge universal agreements on emerging ethical issues. The Organization also
serves as a clearinghouse – for the dissemination and sharing of information and
knowledge – while helping Member States to build their human and institutional
capacities in diverse fields. In short, UNESCO promotes international
co-operation among its 191 [as of March 2005] Member States and six Associate
Members in the fields of education, science, culture and communication."
(Source:
UNESCO website![]()
"The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), established in 1972, works to encourage sustainable development through sound environmental practices everywhere. Its activities cover (...) the promotion of environmental science and information, to an early warning and emergency response capacity to deal with environmental disasters and emergencies."
See also UNEP.Net![]()
![]()
Exposure to contingencies and stress, and the difficulty in coping with them.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ![]()
Soaking of agricultural land caused by a rising water-table [the surface of
groundwater in the soil] or excessive irrigation. [Waterlogging] compacts soil,
deprives roots of oxygen and contributes to
salinization.
(Source: Green 4 Green Glossary![]()
A context- and situation-dependent state, comprising basic material for a good
life: freedom and choice, health and bodily well-being, good social relations,
security, peace of mind, and spiritual experience.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ![]()
Energy derived from wood in various forms. Woodfuel includes
solids (fuelwood and charcoal), liquids (black liquor, methanol, and pyrolitic
oil) and gases from the gasification of these fuels.
(Source: GreenFacts, based on FAO
![]()
The World Bank is a vital source of financial and technical
assistance to developing countries around the world. With the aim to reduce
global poverty and improve living standards, the World Bank provides
low-interest loans, interest-free credit and grants to developing countries for
education, health, infrastructure, communications and many other purposes.
(Source:
World Bank website![]()
"IUCN is a unique Union. Its members from some 140 countries include 77 States, 114 government agencies, and 800-plus NGOs. More than 10,000 internationally-recognised scientists and experts from more than 180 countries volunteer their services to its six global commissions. Its 1000 staff members in offices around the world are working on some 500 projects"
"Our Mission is 'to influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve the integrity and diversity of nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable.' "
GreenFacts is a member of IUCN.
(Source: IUCN website![]()
"The World Health Organization![]()
193 countries and two associate members are WHO’s membership. They meet every year at the World Health Assembly in Geneva to set policy for the Organization, approve the Organization’s budget, and every five years, to appoint the Director-General. Their work is supported by the 34-member Executive Board, which is elected by the Health Assembly. Six regional committees focus on health matters of a regional nature."
WHO's scientific publications are widely recognized as a reference source.
The WHO has a number of regional offices which address the specific issues of those regions.
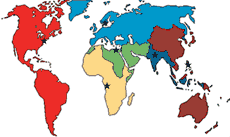
| WHO African Region |
|
| WHO European Region |
|
| WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region |
|
| WHO Region of the Americas |
|
| WHO South-East Asia Region |
|
| WHO Western Pacific Region |

This summary is free and ad-free, as is all of our content. You can help us remain free and independant as well as to develop new ways to communicate science by becoming a Patron!