


The establishment of a forest through tree planting or seeding on land that has lacked forest cover for a very long time or has never been forested. (Source: GreenFacts)
An alien species is a species introduced outside its normal distribution.
Invasive alien species are alien species whose establishment
and spread modify ecosystems, habitats, or species.
(Source:
MA
![]()
The mass of air surrounding the Earth.
The atmosphere consists of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and traces of other gases such as argon, helium, carbon dioxide, and ozone.
The atmosphere plays an important role in the protection of life on Earth; it absorbs ultraviolet solar radiation and reduces temperature extremes between day and night. (Source: GreenFacts)
A small, thin, brown, often flavoured, hand-rolled cigarette that is made in India and other Southeast Asian countries, and consists of tobacco that is wrapped in a tendu leaf. (Source: GreenFacts)
Biodiversity is a contraction of biological diversity. Biodiversity reflects the number, variety and variability of living organisms.
It includes diversity within species (genetic diversity), between species (species diversity), and between ecosystems (ecosystem diversity). (Source: GreenFacts)
The total quantity or mass of organic material produced by living organisms in a particular area, at a given time. (Source: GreenFacts)
A forest that grows in regions of the northern hemisphere with cold
temperatures. Made up mostly of cold tolerant coniferous species such as spruce
and fir.
(Source: LEAF Glossary
![]()
Bushmeat refers to the meat of wild animals.
A colorless, odorless, non-combustible gas, present in low concentrations in the air we breathe (about three hundredths of one percent by volume).
Carbon dioxide is produced when any substance containing carbon is burned. It
is also a product of breathing and fermentation. Plants absorb carbon dioxide
through photosynthesis.
(Source: The Pacific Forest Trust
Glossary![]()
The removal and storage of carbon from the atmosphere in carbon sinks (such as oceans, forests or soils) through physical or biological processes, such as photosynthesis.
Humans have tried to increase carbon sequestration by growing new forests. (Source: GreenFacts)
The quantity of carbon contained in a “pool”, meaning a reservoir or system
which has the capacity to accumulate or release carbon.
(Source: FAO Forestry Terms and
definitions![]()
Occurring over a long period of time, either continuously or intermittently;
used to describe ongoing exposures and
effects that develop only after a long exposure.
(Source:
US EPA
Thesaurus![]()
The long-term fluctuations in temperature, precipitation, wind, and all other aspects of the Earth's climate.
It is also defined by the United Nations Convention on Climate Change as
“change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity
that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to
natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods”
(Source:
CoRIS
glossary![]()
The conversion of forested land to non-forested land as a direct result of
human activities.
(Source: Forest Carbon Accounting
Definitions![]()
A persistent reduction in the capacity to provide ecosystem services.
(Source:
MA
![]()
The variety and relative abundance of different entities in a sample.
(Source:
MA
![]()
The physical, chemical and biological actions or events that link organisms and their environment. (Source: GreenFacts)
The complex system of plant, animal, fungal, and microorganism communities and their associated non-living environment interacting as an ecological unit.
Ecosystems have no fixed boundaries; instead their parameters are set to the
scientific, management, or policy question being examined. Depending upon the
purpose of analysis, a single lake, a
watershed, or an entire region could be
considered an ecosystem.
(Source:
US EPA
Glossary of Climate Change Terms
![]()
Species that face a very high risk of extinction in the wild.
(Source:
MA
![]()
EurActiv is the leading internet portal fully dedicated to European public affairs. It brings together daily EU news, weekly "Update" e-mails, in-depth analysis of selected policy topics, and a directory of 10,000 names of names of people and organizations acting on the EU level, the "Guide". All content is free of charge.
EurActiv aims to "facilitate efficiency and transparency (...) by providing news monitoring, policy positions, discussion forums and contacts on selected EU affairs topics, complementing the existing institutional websites."
(Source: EurActiv website![]()
Any substance that oozes out from the pores of diseased or injured plant tissue.
Resins, gums, oils and lacquers are examples of exudates widely extracted for industrial uses. (Source: GreenFacts)
"The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and debate policy. FAO is also a source of knowledge and information. We help developing countries and countries in transition modernize and improve agriculture, forestry and fisheries practices and ensure good nutrition for all. Since our founding in 1945, we have focused special attention on developing rural areas, home to 70 percent of the world's poor and hungry people. FAO's activities comprise four main areas:
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines “forest” as a portion of land bigger than half a hectare (5 000m2) with trees higher than 5 meters and a tree canopy cover of more than 10 %, or with trees that will be able to meet these criteria.
It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban land use.
Volume of all living trees in a given area of forest or wooded land that have more than a certain diameter at breast height. It is usually measured in solid cubic metres (m3).
It includes the stem from ground level or stump height up to a given top diameter, and may also include branches above a certain diameter.
(Source:
GreenFacts, based on
FAO
Forestry Department
Terms and definitions![]()
The location and environmental conditions in which a particular organism normally lives.
(Source:
MA
![]()
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species assesses the conservation status of species, subspecies, varieties and even selected sub-populations on a global scale.
This system is designed to determine the relative risk of extinction, and the main purpose of the IUCN Red List is to catalogue and highlight those species that are facing a higher risk of global extinction (i.e. those listed as Critically Endangered, Endangered and Vulnerable).
The IUCN Red List also includes information on species that are categorized as
Extinct or Extinct in the Wild.
(Source: based on The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
Introduction![]()
Lac is a natural substance that is secreted by the insect “Coccus lacca” often referred to as the lac beetle. This substance is collected from a variety of trees that play host to the insect. The Lac is taken from the tree branches and bark.
Surface layer on the forest floor of loose non-living organic debris
consisting of freshly fallen or slightly decomposed plant parts (below a certain
diameter), such as leaves, bark, twigs, flowers, fruits, and other vegetable
matter.
(Source: GreenFacts, based on
Alaska Geobotany Center
![]()
A general name for several species of halophyte (plant that grows in soils that have a high content of various salts) belonging to different families of plants (including trees, shrubs, a palm tree and a ground fern) occurring in intertidal zones of tropical and subtropical sheltered coastlines and exceeding one half meter in height.
The term is applied to both the individual and the ecosystem, the latter of
which is termed mangal.
(Source:
CoRIS glossary![]()
A product of biological origin other than wood derived from forests, other wooded land or trees outside forests.
A group or number of people living within a specified area or sharing similar
characteristics (such as occupation or age).
(Source:
ATSDR
Glossary of
Terms![]()
The pronounced deprivation of well-being.
Income poverty refers to a particular formulation expressed solely in terms of
per capita or household income.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
![]()
Production is the process of creating, growing, manufacturing, or improving goods and services. It also refers to the quantity produced.
In economics, productivity is used to measure the efficiency or rate of production. It is the amount of output (e.g. number of goods produced) per unit of input (e.g. labor, equipment, and capital).
In biology, productivity is a measure of the efficiency with which a biological system converts energy into growth. (Source: GreenFacts)
Wood in its natural state as felled, with or without bark. It may be round, split, roughly squared or in other forms.
Roundwood can be used for industrial purposes, either in its round form (e.g.
as transmission poles or piling) or as raw material to be processed into
industrial products such as sawn wood, panel products or pulp.
(Source:
FAO
Forest harvesting Glossary
![]()
A group of organisms that differ from all other groups of organisms and that
are capable of breeding and producing fertile offspring. This is the smallest
unit of classification for plants and animals.
(Source:
OceanLink
Glossary of Common Terms and Definitions in Marine
Biology![]()
Individuals or groups that are affected by a decision and have an interest in
its outcome.
(Source:
TDM Encyclopedia
Glossary
![]()
"Poverty reduction and sustainable development are the principal tasks of the SDC. To facilitate the achievement of these goals, the SDC focuses on various thematic priorities. In each thematic domain, a sub-goal is targeted while ever keeping in mind the fact that the priority themes are intimately linked to one another."
(Source: SDC website![]()
The part of the Earth's surface between the Arctic Circle and the Tropic of
Cancer or between the Antarctic Circle and the Tropic of Capricorn;
characterized by temperate climate [i.e. mild, moderate temperature; neither hot
nor cold].
(Source: WordNet Temperate
zone![]()
A pattern of change over time, over and above short-term fluctuations.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
![]()
Defined by Webster to be the quality of a thing according to which it is thought of as being more or less desirable, useful, estimable or important.
Using this definition the value of an ecosystem might be defined in terms of
its beauty, its uniqueness, its irreplacability, its contribution to life
support functions or commercial or recreational opportunities, or its role in
supporting wildlife or reducing environmental or human health risks, or
providing many other services that benefit humans.
(Source: Ecosystem Valuation
Definition of
Terms![]()
Exposure to contingencies and stress, and the difficulty in coping with them.
(Source:
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ![]()
Energy derived from wood in various forms. Woodfuel includes
solids (fuelwood and charcoal), liquids (black liquor, methanol, and pyrolitic
oil) and gases from the gasification of these fuels.
(Source: GreenFacts, based on FAO
![]()
"The World Health Organization![]()
193 countries and two associate members are WHO’s membership. They meet every year at the World Health Assembly in Geneva to set policy for the Organization, approve the Organization’s budget, and every five years, to appoint the Director-General. Their work is supported by the 34-member Executive Board, which is elected by the Health Assembly. Six regional committees focus on health matters of a regional nature."
WHO's scientific publications are widely recognized as a reference source.
The WHO has a number of regional offices which address the specific issues of those regions.
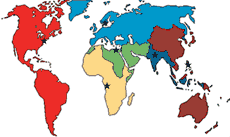
| WHO African Region |
|
| WHO European Region |
|
| WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region |
|
| WHO Region of the Americas |
|
| WHO South-East Asia Region |
|
| WHO Western Pacific Region |

This summary is free and ad-free, as is all of our content. You can help us remain free and independant as well as to develop new ways to communicate science by becoming a Patron!