


The term alcohol refers to a family of chemicals that occur widely in nature and are mass-produced for use in antifreezes, fuels and some manufacturing processes.
Alcohol is commonly used to refer to alcohol-containing drinks such as wine, beer and spirits. In this case the alcohol, ethanol, has been produced by a process called fermentation. Consumption of excessive amounts of alcohol can lead to drunkenness and may be harmful to health. (Source: GreenFacts)
Alcohol Attributable Fractions (AAFs) are used to express the extent to which alcohol contributes to a health outcome, such as alcohol poisoning, non-alcohol poisoning, road traffic injuries, falls, drownings, violence, and other unintentional or intentional injuries. (Source: GreenFacts)
A chronic disease characterized by a
strong craving for alcohol, a constant or periodic reliance on use of
alcohol despite adverse
consequences, the inability to limit drinking, physical illness when drinking is
stopped, and the need for increasing amounts of alcohol to feel its effects.
(Source:
NIH
Understanding Alcohol glossary
![]()
"Alcohol myopia" refers to the tendency of alcohol to increase a person's concentration upon immediate events and reduce awareness of events which are distant (hence the reference to myopia which is nearsightedness).
The study of the chemical processes and compounds occurring in living
organisms.
(Source:
American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering
Glossary![]()
Blood coagulation is the process by which liquid blood changes into semisolid blood clots. It helps preventing blood loss from damaged blood vessels. (Source: GreenFacts)
Any one of a group of diseases that occur when cells in the body become abnormal and have the potential to spread and establish growth in nearby tissues and other parts of the body (malignancy). (Source: GreenFacts )
A disorder affecting the heart muscle [cells] that usually results in the heart being unable to pump effectively.
(Source:
AboutKidsHealth
Glossary![]()
The basic subunit of any living organism; the simplest unit that can exist as an independent living system. There are many different types of cells in complex organisms such as humans, each with specific characteristics. (Source: GreenFacts)
The presence of gallstones in the gallbladder.
(Source: WordNet Glossary![]()
Occurring over a long period of time, either continuously or intermittently;
used to describe ongoing exposures and
effects that develop only after a long exposure.
(Source:
US EPA
Thesaurus![]()
The system that contains the heart and the blood vessels and moves blood
throughout the body. This system helps
tissues get enough oxygen and nutrients, and
it helps them get rid of waste products. The lymph system, which connects with
the blood system, is often considered part of the circulatory system.
(Source:
NCI
Dictionary of cancer
terms![]()
A condition in which the liver is damaged as a result of infection or by certain substances such as alcohol and some medicines.
The damaged liver cells are replaced by scar tissue [the body tissue, usually stronger than the original tissue, remaining after a wound has healed] and the liver becomes hard and filled with fat. This prevents the liver from properly digesting food, metabolizing drugs and making proteins and can result in liver failure and death. (Source: GreenFacts)
Coronary heart disease is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, i.e. a "hardening" of the walls of the small blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart (coronary arteries).
This hardening is due to fatty deposits called plaques that build on the inner walls of these arteries.
The resulting narrowed passageway decreases or stops the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart, which damages the heart muscles and leads to chest pain, shortness of breath, heart attack, and possibly to death. (Source: GreenFacts)
Depression is a mental condition affecting an individual’s mood.
It is characterized by a range of negative feelings such as sadness, loneliness, despair, low self-esteem and guilt.
A depressed person may lose interest in many aspects of life and no longer find pleasure in activities and relationships. (Source: GreenFacts)
Diabetes is a disease that develops when the body is unable to produce or respond to insulin hormone in the normal way. (Source: GreenFacts)
The opening up or enlargement of the blood vessels that is controlled by the action of certain hormones on the muscular lining of the vessels.
This allows more or less blood to flow to particular limbs or organs in response to variations in factors such as activity and temperature. (Source: GreenFacts)
A method of calculating the global or world-wide health impact of a disease or the global disease burden (GDB) in terms of the reported or estimated cases of premature death, disability and days of infirmity due to illness from a specific disease or condition.
(Source:
UN Atlas of the Oceans
GESAMP Glossary![]()
In its most common usage, drunkenness refers to the state of being intoxicated
with alcohol (ie. ethanol) to a degree sufficient to impair mental and motor
functioning.
(Source: GreenFacts, based on Wikipedia
Drunkenness![]()
"The European Commission (EC) embodies and upholds the general interest of the [European] Union and is the driving force in the Union's institutional system. Its four main roles are to propose legislation to Parliament and the Council, to administer and implement Community policies, to enforce Community law (jointly with the Court of Justice) and to negotiate international agreements, mainly those relating to trade and cooperation."
The Commission's staff is organised into 36 Directorates-General (DGs) and
specialised services, such as the Environment DG and the Research DG.
(Source:
EC website![]()
The process by which micro-organisms break down complex organic substances generally in the absence of oxygen to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. (Source: GreenFacts)
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a range of effects that can occur in an individual whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy.
Children with FASDs might have the following characteristics or exhibit the following behaviors:
All FASDs are 100% preventable – if the woman does not drink alcohol while she is pregnant.
(Source: GreenFacts, based on CDCFetal Alcohol Information![]()
The embryo is referred to as a foetus after it has reached a certain stage of
organ development (in humans this is eight weeks after conception).
(Source:
CSIRO
Glossary of
terms![]()
An organ that stores bile after it has been produced in the liver and before it is needed in the intestine where it aids the digestion of fats. (Source: GreenFacts)
Inflammation of the stomach that can be caused by viruses, bacteria and certain substances such as alcohol. Gastritis may cause loss of appetite, discomfort after eating, nausea and vomiting. (Source: GreenFacts)
Glucose is naturally occurring sugar and a primary source of energy for living organisms, including humans. Its chemical formula is C6H12O6. (Source: GreenFacts)
Heavy drinking is a pattern of drinking that exceeds certain standards that are considered moderate or socially acceptable.
Heavy drinking can be defined in various ways, for example:
As used in the GreenFacts Digest on Alcohol, “heavy episodic drinking” refers to drinking occasions leading to drunkenness, often measured as having more than a certain number of drinks on one occasion. (Source: based on the GreenFacts Digest on Alcohol )
Chemical messengers that help our body do different tasks. Hormones are
produced by the endocrine glands and then
sent all over the body to stimulate certain activities. For example, insulin is
a well-known hormone that helps our body digest food. Hormones regulate our
growth, digestion, reproduction and sexual function.
(Source:
EMCOM
Endocrine disruptors
glossary![]()
Inflammation is the reaction of living tissues to infection, irritation or other injury. (Source: GreenFacts)
A hormone made by [certain] cells of the pancreas. Insulin controls the amount
of sugar in the blood by moving it into the cells, where it can be used by the
body for energy.
(Source: St Jude's Children's Hospital: Medical Terminology & Drug
Database![]()
A beer brewed from a bottom-fermenting yeast and given a long cool fermentation.
(Source:
How To Brew
Glossary![]()
Molecules that are a combination of fat and protein and that transports fats and fat-like substances, such as cholesterol, in the blood. (Source: GreenFacts)
Death. Usually the cause (a specific disease, a condition, or an injury) is
stated.
(Source:
ATSDR
Glossary of Terms
![]()
A measure of frequency of occurrence of death in a defined population during
a specified interval of time.
(Source:
CDC
Reproductive Health Glossary
![]()
The nervous system is a complex, sophisticated system that regulates and coordinates body activities.
It is made up of:
A person with power to influence or determine policies and practices at an
international, national, regional, or local level.
(Source: Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ![]()
A condition in which many nerves throughout the body malfunction simultaneously, affecting senses and movements.
It can occur instantly or develop over time. (Source: GreenFacts)
A group or number of people living within a specified area or sharing similar
characteristics (such as occupation or age).
(Source:
ATSDR
Glossary of
Terms![]()
A mental state in which an individual’s contact with reality and thus their ability to relate to other people and their environment is impaired.
It is often caused by false ideas and visions and can result in bizarre behaviors and incoherence.
It is a symptom of several disorders such as schizophrenia and depression.
Psychosis can affect someone temporarily or throughout life. (Source: GreenFacts )
Small glands located in the cheeks that produce and release saliva, the digestive substance, into the mouth. (Source: GreenFacts)
The Scientific Consensus represents the position generally agreed upon at a given time by most scientists specialized in a given field. (Source: GreenFacts)
A stroke is the sudden and instant death of brain cells following an interruption of the blood supply to the brain.
Ischemic strokes generally occur when a blood clot blocks one of the blood vessels in the brain resulting in a temporary or permanent loss of oxygen supply to the brain. They are the most common form of stroke, accounting for 80% of strokes.
Haemorrhagic strokes account for 20% of strokes and are caused by the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain, causing bleeding into the brain tissue and depriving some areas of oxygen.
Depending on the area of the brain affected, a stroke can cause the paralysis of the arms, legs and facial muscles, weakness, loss of vision and speech, unconsciousness, or death. (Source: GreenFacts)
"The World Health Organization![]()
193 countries and two associate members are WHO’s membership. They meet every year at the World Health Assembly in Geneva to set policy for the Organization, approve the Organization’s budget, and every five years, to appoint the Director-General. Their work is supported by the 34-member Executive Board, which is elected by the Health Assembly. Six regional committees focus on health matters of a regional nature."
WHO's scientific publications are widely recognized as a reference source.
The WHO has a number of regional offices which address the specific issues of those regions.
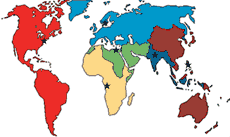
| WHO African Region |
|
| WHO European Region |
|
| WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region |
|
| WHO Region of the Americas |
|
| WHO South-East Asia Region |
|
| WHO Western Pacific Region |

This summary is free and ad-free, as is all of our content. You can help us remain free and independant as well as to develop new ways to communicate science by becoming a Patron!